Do you want to know more about the MScBA Business Analytics & Management programme?
The video below will answer the most frequently asked questions about the programme.
Overview
In the one-year MSc in Business Analytics & Management specialisation, you’ll follow the compulsory core courses in the autumn semester (20 EC). Master electives are offered in Block 2 of the autumn semester (3 EC) and in the spring semester (2x5 EC). The business analytics workshop (6 EC) takes place in January. You’ll work on your master thesis project (18 EC) from February until mid June.
You’ll learn to detect patterns and trends from instructors who each have their own expertise in particular business and management domains. They will train you to apply your analytical skills in each domain. This specialisation of our MScBA programme also benefits from the Erasmus Centre for Data Analytics (ECDA); its network of companies and the on-campus Data Lab provide a rich environment for you to develop your skills and knowledge.
You’ll learn from academics who make meaningful contributions in their fields. Several of RSM’s research groups contribute to the programme, including the departments of Technology and Operations Management, Marketing Management, Finance, and Accounting.
Please note that core courses and electives are subject to change each academic year. While some electives are very popular and we can place most students in the elective(s) of their choice, there are no guaranteed places.
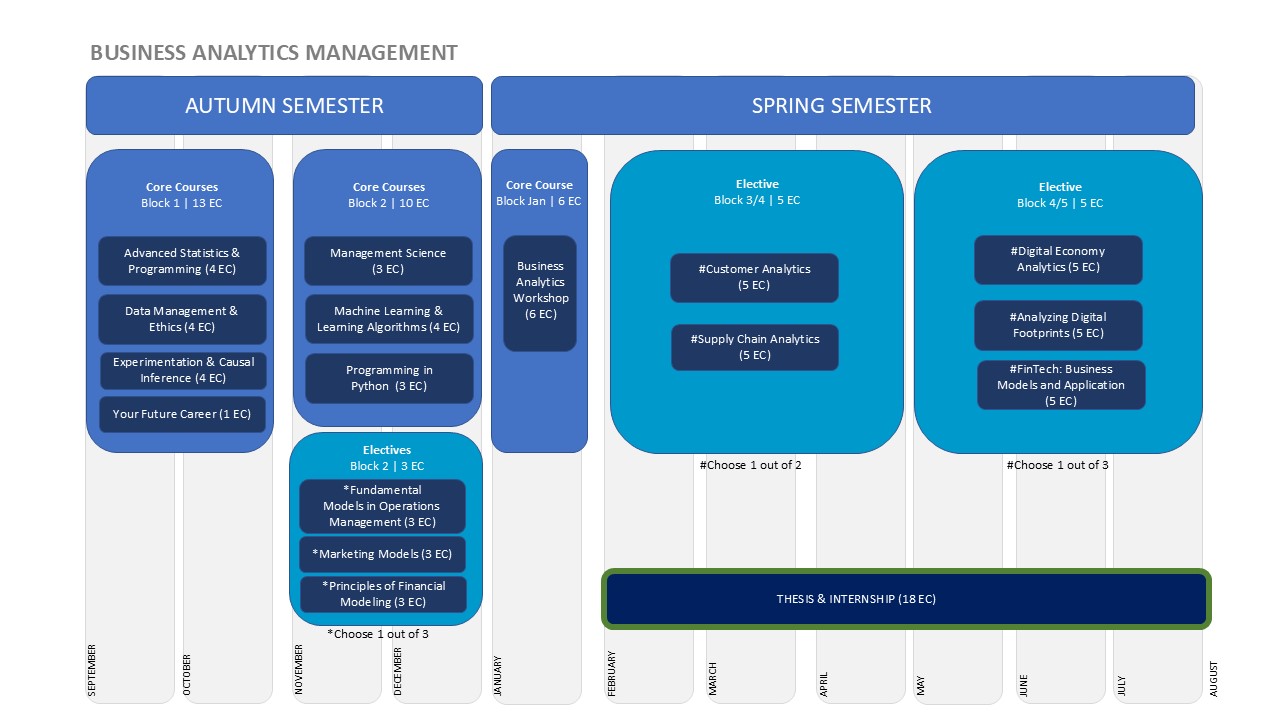
The core courses will fill your analytics toolbox. You will acquire the necessary skills to conduct an analytics project such as programming, data management and experimentation, as well as immerse yourself into the classes about analytics, diagnostic analytics (understanding why something happened), predictive analytics (predicting what will happen), and prescriptive analytics (determining how to make something happen).
- Advanced Statistics and Programming: learn about programming while engaging with advanced statistics (for example general linear models) and vice versa.
- Data Management and Ethics: focus on how to best store and retrieve data and the ethical challenges that come with this.
- Experimentation and Causal Inference: learn what it takes to make causal claims. Topics in this course include experimental design, analyses of experiments, and treatment effects.
- Management Science: learn about constrained optimisation, or more broadly about prescriptive analytics.
- Machine Learning and Learning Algorithms: learn about predicting and how to apply unsupervised and supervised ML techniques.
- Programming in Python: learn the fundamentals of Python programming to analyse and interpret complex business data, enabling data-driven decision-making
- Your Future Career: make crucial steps towards the most suitable career step, whether an internship or a job.
In Block 2 we offer three core electives* that teach you more about specific business domains:
- Marketing
- Operations and Business Information Management
- Finance and Accounting
Each of these courses familiarises you with core models in the respective business domains, relevant challenges, and some of the analytics used to tackle these. You will have the opportunity to follow two out of the three offered electives, substantially broadening your business knowledge.
In the electives in Block 2 through 5, which run in parallel to the thesis trajectory, you can select two electives that either focus on a specific class of analytics tools with broad application or a business domain with a specific set of analytics tools.
A list of electives can be found below:
- Supply Chain Analytics
- Marketing Models
- Principles of Financial Modelling
- Customer Analytics
- Digital Economy Analytics
- Analysing Digital Footprints
- FinTech: Business Models & Applications
*Please note that certain electives may be very popular. Although we can place most students in the elective(s) of their choice, there are no guaranteed places.
For a detailed description of all of the courses including electives, please view the course catalogue (for reference only, catalogue continually updated throughout the year).
Learn more
You can get a taste of working life – from large multinationals to fast-growing start-ups – by applying your new wealth of knowledge to a real company problem during your internship, which is optional in your programme. The RSM Career Centre will support you in finding a suitable position. Many students acquire their first job after graduation from the contacts they make during their internship.
Explore the world and broaden your study experiences by going on international study trips and exchanges at other top schools. RSM has an extensive partner school network of more than 100 business schools and universities worldwide, including top business schools such as ESADE in Barcelona and The Wharton School in the USA. An international exchange is an optional element after you’ve studied for your master for at least one year.
Business Analytics & Management is a new specialisation of our MScBA designed to fulfil the growing business demand for graduates with strategic business and management skills who can create business benefits using advanced analytics. RSM master graduates combine intellectual curiosity with practical skills geared towards creating positive change in business. In our most recent survey, more than 90 per cent of all RSM graduates find a job within six months of graduating – in many cases even before they graduate. Students choosing this master programme may consider career paths as:
- Data scientist
- Business analyst
- Financial analyst
- Supply chain analyst
- Marketing analyst
- Financial modeller
- Customer journey specialist
- Omni-channel specialist
- Assortment and pricing specialist
Our graduates enter a range of industries including retail, banking, insurance, and consulting. They typically enter in advanced starting roles where they become part of a team of analysts that works closely with the problem owners, the people on the business side whose practices they are trying to improve and simplify through the use of analytics. Our graduates also often serve as bridges between the business and functions such as data engineering.
Curious to see what our alumni are doing?
Good to know
Non-EEA nationals who have earned a diploma from a higher education institute in the Netherlands can apply for a special residence permit called the orientation year after completing their studies. The 'Orientation Year for Graduates Seeking Employment' is a residence permit aimed at retaining foreign talent for the Dutch labour market. During this orientation year you are free to work without a work permit. Participants who find a job during this period can change their orientation year into a residence permit for Highly Skilled Migrants under more favourable terms.
For the most up-to-date information please visit the following website.
What's next after your studies? The RSM Career Centre is your guide for an impactful career. Its expertise in the labour market, personal branding and connections with employers will prepare you for your business career. Get ready for some exciting job fairs, workshops, speed interviews and coaching. You may land your first internship or job before you even graduate!
You’re a member of the RSM community from Day 1. After you graduate, you’ll also be a member of the RSM alumni network. The countless benefits include networking events worldwide with local chapters, lifelong learning and professional development, mentoring opportunities and access to the latest business knowledge and research. Your study at RSM is the first step towards being part of this inspiring community that you’ll be part of forever.
Talk to our current students!
The 2025-2026 tuition fee for the MSc programmes is approximately €24,600 for non-EEA students. The Dutch government contributes towards this cost for students who hold a nationality from a country belonging to the European Economic Area (EEA). These students therefore only pay the statutory fee €2,601 in 2025-2026.
For EEA nationals who have already completed a master in the Netherlands (and obtained the diploma) the tuition fee for a 2nd master is approximately €14,400.
Please note that all these tuition fee tariffs are subject to change.
There are other costs associated with the Master programmes, for more information please review the “Other expenses” section below thoroughly.
Scholarships
The number of scholarships is limited and mainly merit based. If a scholarship covers only the tuition fees, be aware that you need to finance your own living expenses (rent, food and insurances) for the duration of your studies. RSM does not offer scholarships for the pre-master programme. We do however offer a maximum of 2 scholarships per academic year to RSM pre-master students enrolling in an MSc programme.
Rotterdam School of Management, Erasmus University (RSM) offers multiple scholarships to prospective students from non-EEA countries who are not entitled to pay the EEA tuition fee, provided their grades are considered ‘excellent’. RSM also offers one scholarship, the Erasmus Trustfonds Scholarship, to students from EEA countries.
Besides scholarships awarded by RSM, there are also scholarships awarded by the Dutch government or other organisations that are available if you meet certain criteria such as nationality, age, etc We have listed some of them below but we encourage you to use resources such as Grantfinder or the Scholarship Portal to find additional scholarships.
- StuNed
- G&D Europe Scholarship
- NN Future Matters Scholarship
- Russia: The Global Education Programme
- LPDP
- OKP
Scholarship tips
- Contact the Ministry for Higher Education in your home country to see whether there are scholarship options.
- We have virtual information session covering all you need to know about scholarships and financial aid. Watch it here.
For students from the Netherlands or the EU/EEA, it may be possible to apply for limited funding towards payment of your tuition fees. Find out whether you meet the nationality and age requirements and read more information about the application process here.
IM/CEMS is a program that - if you are still eligible - entitles you to a maximum of 1 year's use of your DUO entitlements. Students who have received a basic grant and possibly a supplementary grant from DUO in the first year of IM/CEMS and meet the following additional conditions may be eligible for an additional half year (6 months) of financial support, which is equal to the grant received in the last month during the program. Please contact the student counselors for more information.
Conditions Financial Support Fund
Students eligible for financial support due to extended master programmes are those who:
a) are enrolled full-time in a public funded Erasmus University Rotterdam degree programme, which is extended on the base of article 7.4, paragraph 8 of the Dutch Higher Education and Research Act;
b) are enrolled as first enrollment (hoofdinschrijving) in the study programme as referred to under a, for which the student pays statutory tuition fee;
c) for this program, is or was entitled to study finance (prestatiebeurs hoger onderwijs) as referred to in the Wet Studiefinanciering 2000, and during the period corresponding to the study load that exceeds 60 ECs, and is no longer eligible for student finance in the form of an additional grant.
Other expenses
After having filled in all of the necessary application information on the Online Application Form (OLAF) and uploaded the required documents, applicants with a degree obtained outside the Netherlands will be asked to pay a non-refundable €100 handling fee. This fee can be paid online via the Erasmus Payment System which uses either iDEAL (for those with a Dutch bank account) or PayPal (which can be linked to any bank account or credit card worldwide). It is important that applicants complete the payment process as indicated, otherwise the system cannot register the payment.
The additional expenses in addition to tuition and general living costs (see below) vary per programme and may include:
- Study materials such as books, readers and business cases
- Costs involved in kick-off meetings
- Costs related to travel, international excursions and compulsory exchange semesters or internships abroad
Approximately € 300 - 500 (per year), these costs differ per programme.
For a reasonable standard of living in the Netherlands, you should have an income of between €1,235-€1,735 per month depending on your lifestyle. Further information about the costs of living in the Netherlands and related subjects can be found on this website. Below is an example of monthly expenditures:
| Furnished accommodation, including gas and electricity | € 500-1,000 |
| Medical insurance | € 50 |
| Telephone/internet | € 15-40 |
| Food | € 300 |
| Books, recreation, clothing | € 300 |
| Public Transportation | € 50 |
| Total | € average 1235 - 1735 |
| Other potential expenses: | |
| Buying or renting a bike | € 100 - 250 (per year) |
| In private residence (not student housing) yearly municipal and water taxes | € 100 - 300 (per year) |
| Study trip or other study related travel | € 300 - 500 (per year) |
Please ensure, prior to your arrival at RSM, that you have or will have sufficient funding available to finance your stay at RSM. Finding a part-time job, may be an option, but can not be guaranteed. You should therefore not rely on finding other ways to supplement your income during your studies. For additional information on obtaining a part-time job, visit the website of the Nuffic.
For EEA students there are no formal restrictions in finding work in the Netherlands, but students with a lack of Dutch language skills will find it difficult to secure employment. Non-EEA students are subject to labour regulations, which makes the likelihood of obtaining a work permit very small. We therefore ask students not to rely on this possibility. We do not encourage students to combine studies with the heavy workload from a part-time job.
On this page we have listed the minimum admissions requirements. Please read the information carefully before moving to the application process. Also make sure to check out our extensive Frequently Asked Questions section.
This maximum for the 2025 intake was reached at 12:50 on 1 October and this application is currently CLOSED. The application for the 2026 intake will open on 1 October 2025. This is a capped programme, which means that the maximum number of applications we accept is 292.
Find out everything you need to know about entry visas & residence permits for non-EU or EEA students at RSM.
Finding housing in Rotterdam can be tricky. To help you in your search for housing, we have compiled some helpful resources







